
Hash란
Key-value쌍으로 데이터를 저장하는 자료구조입니다.
Unordered maps
are associative containers that store elements formed by the combination of a key value
and a mapped value,
and which allows for fast retrieval of individual elements based on their keys.
Internally, the elements in the unordered_map are not sorted in any particular order with respect to either their key or mapped values, but organized into buckets depending on their hash values to allow for fast access to individual elements directly by their key values (with a constant average time complexity on average).
💊 멤버 함수
| Member functions | definition | example | |
| - | - | - | #include <unordered_map> unordered_map<string, int>example; // unordered_map<KEY, VALUE> |
| capacity | empty | - | example.empty( )? yes : no; |
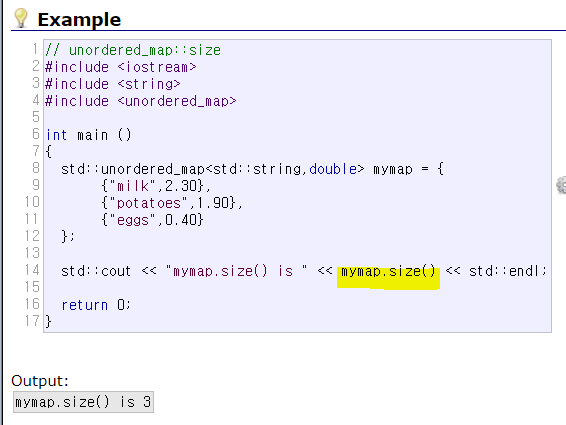
| size | 요소 수를 계산합니다. | example.size( ); | |
| Iterators | begin | 처음에 대한 반복자를 return합니다. | example.begin( ); |
| end | last + 1의 원소를 return합니다. | example.end( ); | |
| Element access | at | 지정된 키 값이 있는 요소에 접근합니다. | example = { {"Mars" 3000} , {"Jupiter", 7000} }; example.at( "Mars" ) = 25; > example 내의 Mars의 value는 25로 바뀝니다. |
| Element lookup | find | Get iterator to element | example.find( "Mars" ); find 함수의 경우 만일 해당하는 원소가 존재한다면 이를 가리키는 반복자를, 없다면 end 를 리턴합니다. |
| count | Count elements with a specific key (find와 동일) |
example.count( "Mars" ) | |
| Modifiers | insert | Insert elements | example.insert({"three", 3}); example.insert(make_pair("four", 4)); |
| erase | Erase elements | example.erase( example.find( "Hi" ) ); 간단히 find 함수로 원소를 가리키는 반복자를 찾은 뒤에, 이를 전달하면 됩니다. |
+ capacity 출력 함수 비교
| size ( ) | bucket_count( ) |
 |
 |
📖 예시
1. 기본 예제
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// Create an unordered_map of three strings (that map to strings)
unordered_map<string, string> u = {
{"RED","#FF0000"},
{"GREEN","#00FF00"},
{"BLUE","#0000FF"}
};
// Iterate and print keys and values of unordered_map
for( const auto& n : u ) {
cout << "Key:[" << n.first << "] Value:[" << n.second << "]\n";
}
// Add two new entries to the unordered_map
u["BLACK"] = "#000000";
u.insert({"WHITE", "#FFFFFF"});
// or
// u.insert(make_pair("WHITE", "#FFFFFF"));
// Output values by key
cout << "The HEX of color RED is:[" << u["RED"] << "]\n";
cout << "The HEX of color BLACK is:[" << u["BLACK"] << "]\n";
}
2. 활용 예제
코딩테스트 연습 - 완주하지 못한 선수
수많은 마라톤 선수들이 마라톤에 참여하였습니다. 단 한 명의 선수를 제외하고는 모든 선수가 마라톤을 완주하였습니다. 마라톤에 참여한 선수들의 이름이 담긴 배열 participant와 완주한 선수
programmers.co.kr
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
string solution(vector<string> participant, vector<string> completion) {
string answer = "";
unordered_map<string, int> strMap;
for(auto elem : completion)
{
if(strMap.end() == strMap.find(elem)) // 현재 맵에 elem 값이 없다면
strMap.insert(make_pair(elem, 1));
// make_pair(변수1, 변수2) : 변수1과 변수2가 들어간 pair 생성
else
strMap[elem]++;
}
for(auto elem : participant)
{
if(strMap.end() == strMap.find(elem))
{
answer = elem;
break;
}
else
{
strMap[elem]--;
if(strMap[elem] < 0)
{
answer = elem;
break;
}
}
}
return answer;
}
코딩테스트 연습 - 전화번호 목록
전화번호부에 적힌 전화번호 중, 한 번호가 다른 번호의 접두어인 경우가 있는지 확인하려 합니다. 전화번호가 다음과 같을 경우, 구조대 전화번호는 영석이의 전화번호의 접두사입니다. 구조
programmers.co.kr
reference
unordered_map - C++ Reference
1234 unordered_map ::iterator it; (*it).first; // the key value (of type Key) (*it).second; // the mapped value (of type T) (*it); // the "element value" (of type pair )
www.cplusplus.com
unordered_map 클래스
`unordered_map`다양 한 길이의 요소 시퀀스를 제어 하는 c + + 표준 라이브러리 컨테이너 클래스에 대 한 API 참조입니다.
docs.microsoft.com
'OLD_알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| STL ] Queue (0) | 2021.02.10 |
|---|---|
| STL ] vector에서 iterator 사용 - 타 블로그 참고 (0) | 2021.02.03 |
| Solving Skill ] 해시 맵(Hash Map) (0) | 2021.01.22 |
| Solving Skill ] Greedy (0) | 2021.01.17 |
| C++ ] 문자열(string, char) (0) | 2021.01.08 |



댓글